Fix Task Manager Disabled by Administrator – 5 Ways to Open
If you’re unable to access Task Manager on your Windows computer due to administrator restrictions, don’t worry. In this article, we’ll explore five different ways to open Task Manager and get back to managing your tasks efficiently.
Understanding the “Task Manager Has Been Disabled By Your Administrator” Error
If you’re seeing the “Task Manager Has Been Disabled By Your Administrator” error, don’t worry – there are several ways to fix it. Firstly, try using the keyboard shortcut of Ctrl + Alt + Del to open the Task Manager. If that doesn’t work, try right-clicking on your computer’s taskbar and selecting “Task Manager” from the list.
If both of these options are greyed out, your administrator may have disabled the Task Manager through group policy. In this case, you’ll need to use the Command Prompt or Registry Editor to enable the Task Manager. Be cautious when using these methods, as editing system settings can cause issues if done incorrectly.
Reasons for Task Manager Being Disabled
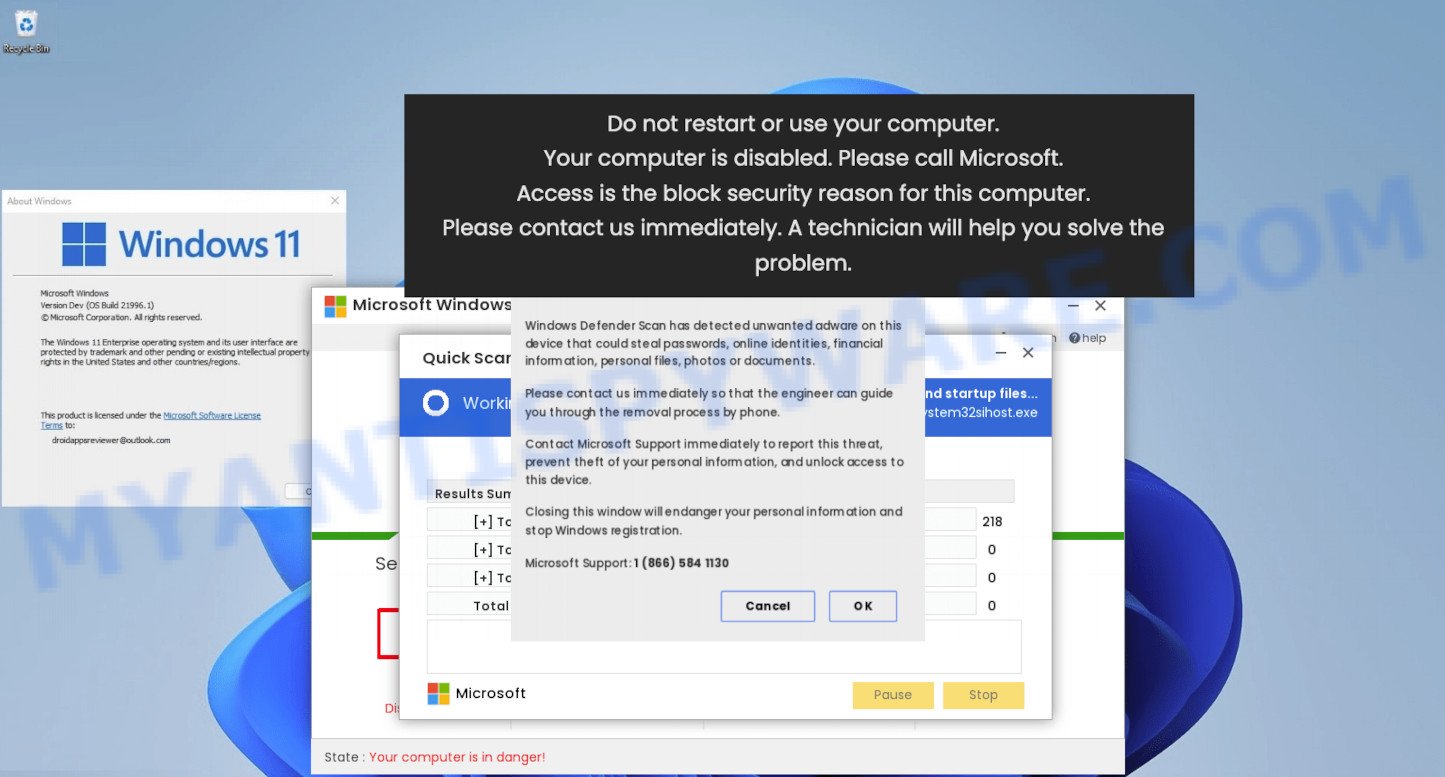
- Virus or Malware: A malicious program can disable task manager to prevent you from terminating it or any related processes.
- Group Policy Settings: Your administrator may have disabled task manager through group policy settings.
- System File Corruption: Missing or corrupted system files can cause task manager to be disabled.
- Registry Edit: A registry edit may have been made to disable task manager as a security measure.
- Third-Party Antivirus Software: Some antivirus software may disable task manager as a security feature.
Fixing Task Manager Using Local Group Policy Editor, Command Prompt, Registry Editor, and Registry File
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Local Group Policy Editor | Accessing the Group Policy Editor to enable Task Manager |
| Command Prompt | Using the command prompt to enable Task Manager |
| Registry Editor | Accessing the registry editor to enable Task Manager |
| Registry File | Enabling Task Manager by importing a registry file |
It can even identify hardware malfunctions that may be contributing to the problem. Additionally, Fortect offers OS recovery, restoring vital system files without affecting user data.
Getting Rid of Malware to Enable Task Manager
If your Task Manager is disabled by an administrator, it may be due to malware on your computer. The first step to fixing this issue is getting rid of any malware.
To do this, run a full virus scan using your antivirus software. If the scan detects any malware, follow the instructions to remove it.
Once the malware is removed, you can try to open Task Manager using Ctrl + Alt + Del and selecting Task Manager from the options. If this doesn’t work, try opening Task Manager by typing “taskmgr” into the Run window.
If you’re still unable to open Task Manager, you may need to perform a system restore or reinstall Microsoft Windows. Remember to always keep your antivirus software up-to-date to prevent future malware infections.
Enabling Task Manager on PC with Administrator Access
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type gpedit.msc and press Enter.
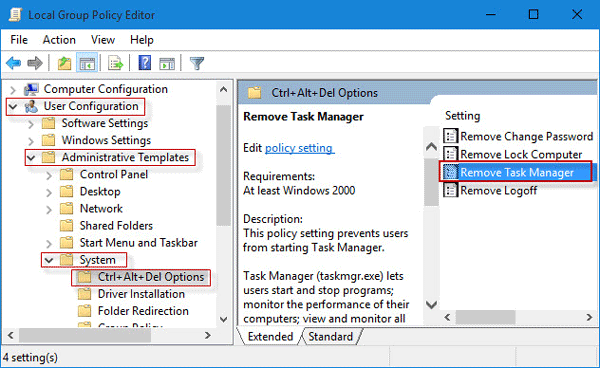
- Go to User Configuration and select Administrative Templates.
- Click on System.
- Double-click on Ctrl+Alt+Delete Options.
- Look for Remove Task Manager and double-click on it.
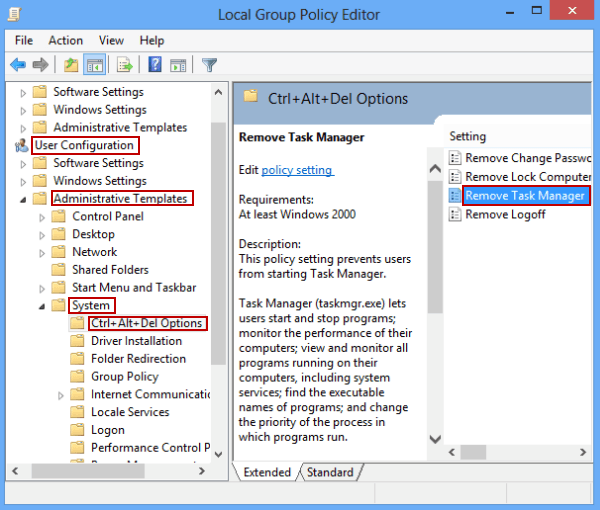
- Select Disabled and click OK.
Method 2: Using Registry Editor
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type regedit and press Enter.

- Go to HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System.
- Double-click on DisableTaskMgr.
- Change the value to 0 and click OK.
Method 3: Using Command Prompt
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type cmd and press Enter.

- Type taskmgr /reg and press Enter.
Method 4: Using Task Manager Fix Tool
- Download and install Task Manager Fix Tool.
- Run the tool and click Enable Task Manager.
Method 5: Using System Restore
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type rstrui and press Enter.

- Select a restore point when Task Manager was working.
- Follow the prompts to restore your system.
Common Issues with Disabling Task Manager
Common issues with disabling the Task Manager include not being able to end unresponsive programs, not being able to monitor system performance, and not being able to identify and stop malicious processes. This can happen if the administrator of a system disables it to prevent unauthorized changes or to limit access. If you encounter a disabled Task Manager, there are several ways to open it.
One way is to use the Ctrl + Alt + Delete keys and then click on Task Manager. Another way is to right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager. If you are using Microsoft Windows 10, you can also search for Task Manager in the Start menu. In some cases, the Task Manager may be greyed out or grayed out, which may indicate that it has been disabled by a system administrator or group policy. If you are using a Windows Server or are in a school or work environment, you may need to contact your IT department to re-enable Task Manager.
Ensuring Task Manager is Running for Efficient PC Performance
To ensure efficient PC performance, it’s important to have Task Manager running. If it’s disabled by an administrator, there are five ways to open it.
1. Press Ctrl + Alt + Delete to access the Task Manager.
2. Use the Run dialog box by pressing Windows key + R and typing “taskmgr”.
3. Open the Start menu, type “task manager”, and click on the result.
4. Use the Command Prompt by typing “taskmgr” and press Enter.
5. Use the PowerShell by typing “taskmgr” and press Enter.
If you’re using Windows 10 or Windows Server, the Task Manager might be grayed out if you’re not an administrator. In this case, contact your IT department to enable it. If you’re using a school computer, ask your teacher or IT administrator for assistance.
Warning: The task manager has been disabled, which may prevent you from monitoring and managing running processes on your computer. Download this tool to run a scan